Specific Heat Capacity of Copper
I Heat capacity Mass Specifc heat capacity 150 10 3 k g 410 J k g K 615 J K The heat capacity of copper is 615 JK ii QmcΔT where. The specific heat of carbon steel is 049 kJkgC and the heat required can be calculated as.
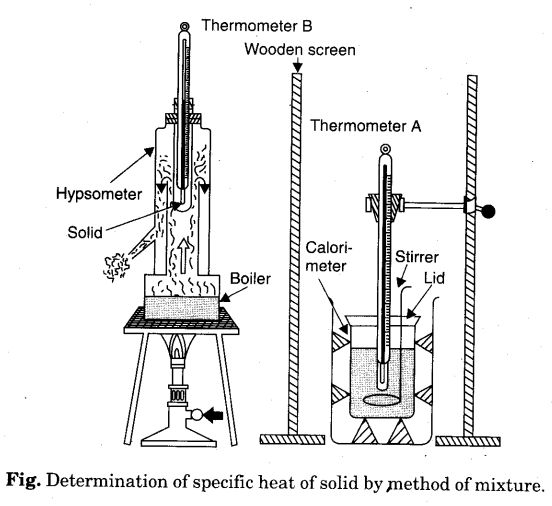
To Determine Specific Heat Capacity Of A Given Solid By Method Of Mixtures
Calculate specific heat as c Q mΔT.

. Heat capacity is the quantity of heat absorbed emitted whole body in the process of heating cooling by 1 Kelvin. The specific heat capacity and volumetric heat capacity wi. Determination of Specific Heat Capacity of Copper Introduction.
Specific heat of Copper is 038 Jg K. The specific heat capacity of copper and iron are 0385 Jg oC 0129 JgoC respectively. Specific heat is a physical quantity.
A substance having a small value of specific heat capacity requires a small amount of heat for a raise in temperature. Copper Specific Heat Latent Heat of Fusion Latent Heat of Vaporization. On the lin-lin plot you can clearly.
Thus it becomes suitable. It means that it takes 04 Joules of heat energy to raise the temperature of one gram of copper by one. Material Water Aluminium Steel Copper Brass Specific Heat capacityJkg-1C-1 41813 897 420 385 375 From this I can see that my initial prediction.
I have sorted them in decreasing order. Specific heat of copper. 71 rows Related Resources.
2 Link with the specific heat capacity. Heat capacity Attached you will find a file CvCu containing the molar heat capacity of copper. For illustration the specific heat capacity of nanofluid made by ethylene glycol and copper dioxide nanoparticle.
Q m c T f - T i or Q mc T The value of c al for aluminum is 0215calg oC. The heat added to warm or subtracted to cool is given by. Jewett September 10 2010.
Make plots of the heat capacity on lin-lin and a log-log scales. Determination of the Specific Heat Capacity of Copper Metal Using Calorimetry by Joe Student Partner. Material Properties - Material properties of.
The fact that copper has a specific heat capacity of 04 jg-1 K-1. Before the specific heat capacity of copper can be determined it is necessary to know the heat capacity of the calorimeter. In our example it will be equal to c -63000 J 5 kg -3 K 4200 J kgK.
The value can be found by performing an experiment with a metal. The specific heat of water is 100 calgoC. This is the typical heat capacity of water.
The specific heat c of a material is defined to be the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of the. Latent Heat of Fusion of Copper is 1305 kJmol. Heat lost by the pennies is equal to heat gained by the water in the calorimeter.
Mary Student Chemistry 121 Mr. Q - heat absorbed m - the mass. Materials Specific Heat Capacity of Metals Table Chart.
2 kg of carbon steel is heated from 20 oC to 100 oC. Given that q mcT calculate the heat gained in J by water. The specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of heat J absorbed per unit mass kg of the material when its temperature increases 1 K or 1 C and its units are.
The same amount of energy applied to equal masses of copper and iron will result in a. 55 rows The table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials and when applicable.

How Do The Specific Heats Of Metals Compare With Water Socratic Heat Methylation Water

To Determine Specific Heat Capacity Of A Given Solid By Method Of Mixtures

Find Specific Heat Physics Help Physical Properties Of Matter Physics

Specific Heat Of Water Very High So It Takes More Energy To Increase The Temperature Of A Given Mass Of Wat Teaching Science Science Facts Homeschool Science
0 Response to "Specific Heat Capacity of Copper"
Post a Comment